
Table of Contents
ToggleNCERT Solution For Class 9, Science, Chapter 5, The Fundamental Unit Of Life, is study of cell which is the fundamental organizational unit of life. Class 9, Science, chapter 5 involves topic related structure and working process of cell which is very important for further studies.
NCERT Solution For Class 9, Science, Chapter 5, The Fundamental Unit Of Life
Chapter 5, The Fundamental Unit Of Life
Intext Questions
Page No.59
Q.1. Who discovered cells, and how?
Ans: The cell was discovered by Robert Hook, in 1665. He discovered cell in a cork slice with the help of primitive microscope.
Q.2. Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
Ans: (a) In all living organisms Whether as large as elephant or as small as bacteria, it is the cell which constitute the body. Hence, it is called structural unit of life.
(ii) In all living organisms, it is the cell which, performs various life functions such as nutrition, Excretion, respiration, etc. Hence, it’s called the functional unit of life.
Page No. 61
Q.1. How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss.
Ans: The substances move from place of higher concentration to the place of lower concentration in a cell. This process is known as diffusion. Substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell by diffusion. Thus, When the concentration of CO2 in the external environment of the cell is higher than that inside the cell, CO2 moves inside the cell.
When the concentration outside the cell becomes low and it is high inside the cell due to metabolic reactions, the CO2 moves out.
In same way water also moves outside and inside the cell.
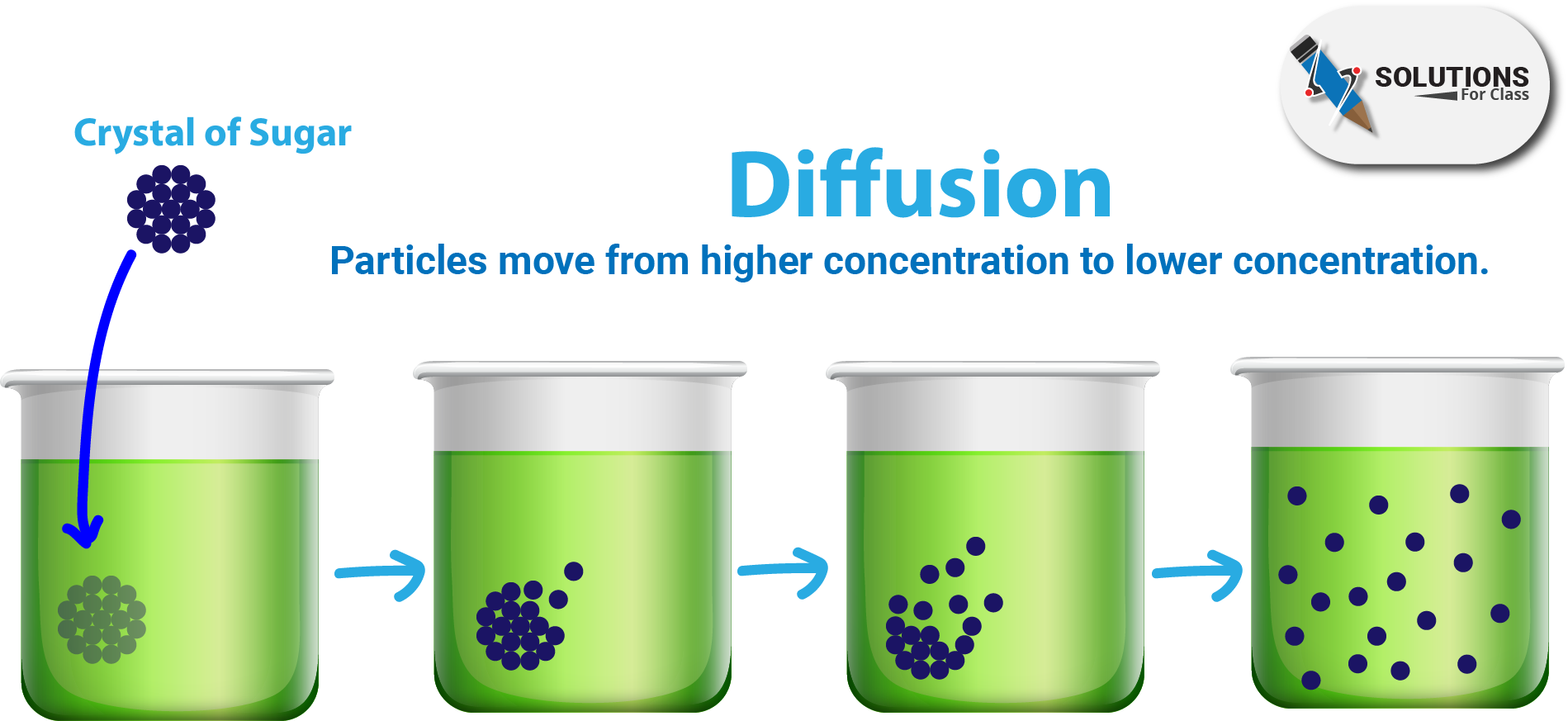
Q.2. Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane?
Ans: Plasma membrane is called as a selectively permeable membrane, because it allows only certain molecule to pass through the cell membrane. like oxygen, carbon dioxide, minerals some proteins etc. while at the same time it blocks other material from entering through it.
Page No. 63
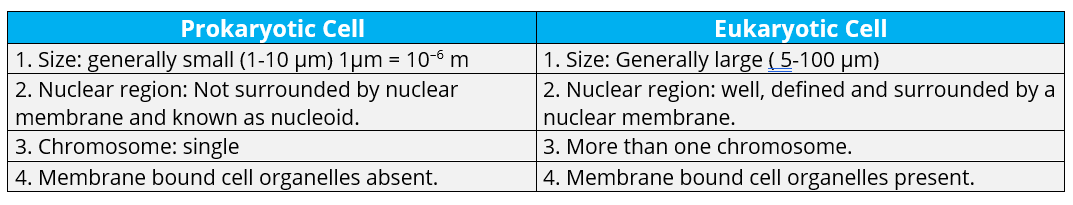
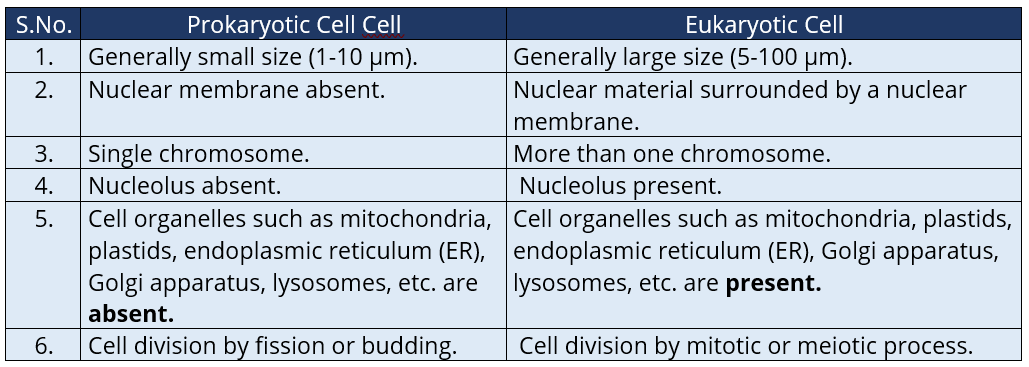
Q.1. Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
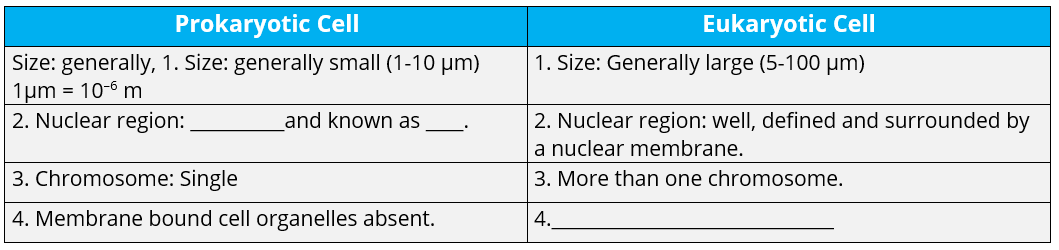
Ans:
Page No. 65
Q.1. Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
Ans: (i) Plastids (ii) Mitochondria
Q.2. If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen?
Ans: if the structure of a cell is destroyed. the cell will not be able to perform its basic functions, such as respiration and nutrition, and will not be able to synthesise protein. This may stop all the life activities of the organism and may result in its death.
Q.3. Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags?
Ans: Lysosomes are able to do this because they contain powerful digestive enzymes capable of breaking down all organic material such bacteria or food as well as old organelles. when the cell is destroyed, the lysosomes explode and their enzymes digest (eat) their own cell. Therefore, lysosomes are also known as the ‘suicide bags’ of a cell.
Q.4. Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
Ans: The proteins are synthesized in the Ribosome inside the-cell.
Page No. 67
Q.1. Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
Ans:
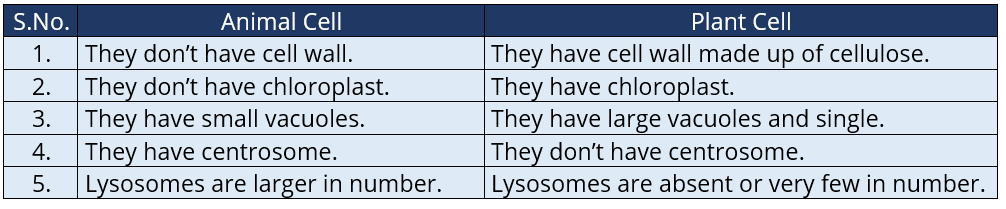
Q.2. How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
Ans:
Q.3. What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
Ans: Plasma membrane is the Outer covering of the cell that separates its components from the surrounding medium. The plasma membrane allows the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cell. works as a selectively permeable membrane. If it ruptures or breaks down the cytoplasm would be exposed to the external environment. and the process of allowing entry or exit materials would be stopped.
Q.4. What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
Ans: If the cell does not have golgi apparatus, the material synthesised near the ER (Endoplasmic reticulum) will not be packaged and dispatched to various targets inside and outside the cell. and also, Lysosomes will not be formed. As result, there will be no excretion of waste matter.
Q.5. Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
Ans: Mitochondria are called the ‘Powerhouse of the cell’. They produce energy which is stored in the form of ATP molecules. This energy is required for different activities of life.. That is why, mitochondria are called powerhouse.
Q.6. Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
Ans: The lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane are synthesized in the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER).
Q.7. How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
Ans: Amoeba obtains its foods by the process of phagocytosis. The cell membrane of amoeba is projected into numerous fingers like outgrowths called pseudopodia. Amoeba surrounds a food particle by pseudopodia and makes a food vacuole after engulfing the food. when the particle is completely trapped the amoeba secretes digestive enzymes that digests the food. Thus, the amoeba obtains it’s food.
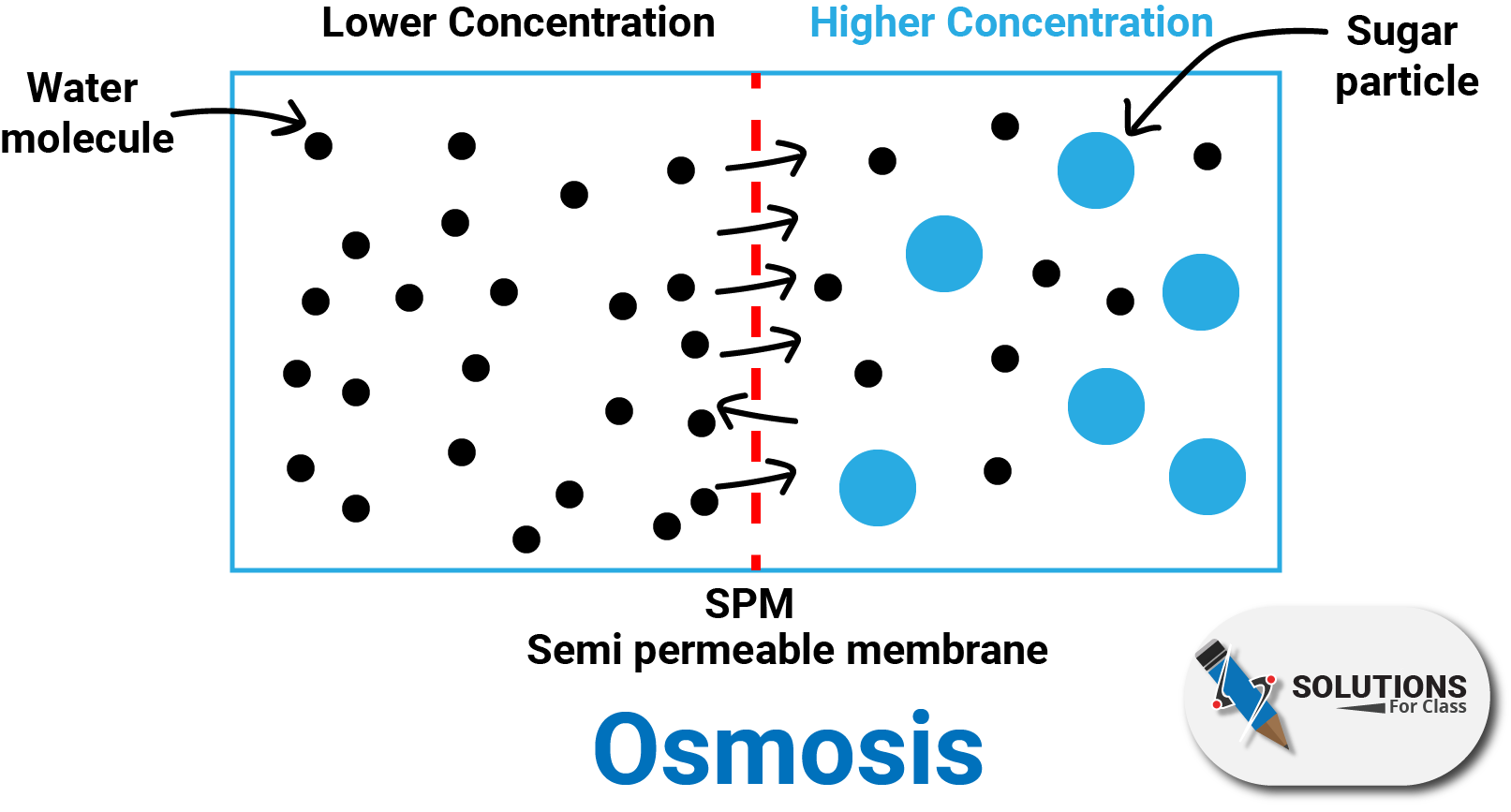
Q.8. What is osmosis?
Ans: The process in which water moves from lower concentration to higher concentration through Semi permeable membrane called as osmosis.
Q.9. Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoos each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed-out portions of A and D.
Ans:(i) Since sugar and salt was present in B and C respectively, water due to osmosis, water moves towards the inside of potato from its outside. As a result, water collects inside cups B and C.(ii) Cup A is important in this experiment because it Shows that if two solutions with the same concentration are, taken, then there is no movement in the water molecules.
(iii) Water does not gather inside cups A and D because cup D is made of boiled potato. Its cells are dead and their cell membrane are no more selectively permeable. Therefore, no osmosis takes place and water does not go inside the potato from outside.
Potato cup A has been left empty. Therefore, the concentration on the both side of the cell membrane is equal. As a result, there is no movement in the water molecules. Thus, water does not collect inside cups A and D.
Q.10. Which type of cell division is required for growth and repair of body and which type is involved in formation of gametes?
Ans: (i) Cells divide by mitosis for growth and repair.
(ii) And meiosis to produce gametes for sexual reproduction.

